In the ever-changing landscape of the insurance industry, characterized by the dominance of data-driven choices and personalized customer experiences, Generative AI has emerged as a powerful driver of innovation. In this rapidly evolving environment, insurance providers are challenged to create inventive solutions that meet customer expectations and improve operational effectiveness. Generative AI, with its unique capabilities, is currently exerting a significant influence on the insurance sector. It is not only transforming conventional practices but also reimagining the way insurers manage their operations.
Generative AI empowers insurance companies to leverage advanced machine learning models, enabling the development of tailored recommendations and customized products for their customers. It also allows for precise calculation of individualized pricing, all while ensuring a high level of customer satisfaction. This data-centric approach not only improves insurers’ decision-making abilities but also streamlines the digital purchasing process for policyholders, making it quicker and more user-friendly.
Moreover, the operational efficiency of an insurance enterprise is pivotal to its success, and generative AI assumes a central role in aiding insurers in attaining this objective. By harnessing AI-powered task automation, insurance providers can make substantial strides in enhancing their operational efficiency. This, in turn, enables insurers to react swiftly, diminishes the need for manual interventions, and results in the delivery of superior customer experiences.
Generative AI’s ability to generate fresh and synthetic data is another game-changer. This unique capability empowers insurers to make faster and more informed decisions, leading to better risk assessments, more accurate underwriting, and streamlined claims processing. With generative AI, insurers can stay ahead of the curve, adapting rapidly to the ever-evolving insurance landscape.
Within the article, we will undertake a thorough examination of how generative AI is shaping the insurance industry, revealing its wide ranging applications, tangible advantages, and real-life instances that illustrate its transformative impact.
- An Overview of Generative AI in the Insurance Industry.
- Highlighting the Differences Between Traditional and Generative AI in Insurance Operations: Key Differences.
- Various Generative AI Models Applied to the Insurance Industry.
- Advantages of Generative AI in the Insurance Industry.
- Applications of Generative AI in the Insurance Industry.
- Real-world Examples: How Insurance Companies Employ Generative AI.
- Prospects of Generative AI in the Insurance Industry.
An Overview of Generative AI in the Insurance Industry.
Generative AI represents a subset of AI technology, empowering machines to generate fresh content, data, or information resembling human-produced output. Unlike traditional AI systems dependent on predefined rules and patterns, generative AI harnesses advanced algorithms and deep learning models for the creation of original and dynamic results. In the context of the insurance sector, generative AI assumes a pivotal role in reshaping numerous facets, spanning customer interactions, risk evaluation, and fraud detection. Generative AI ushers in a new era within the insurance domain, presenting unprecedented opportunities for innovation and expansion. Its capacity to originate content and glean insights from data paves the way for pioneering applications specific to this industry. This facilitates predictive modeling, enabling the formulation of risk scenarios that empower insurers to proactively manage potential risks.
Furthermore, generative AI’s aptitude for crafting personalized content empowers insurers to provide tailor-made insurance policies and experiences, fostering deeper connections with their clientele.
Prospects of Growth for Generative AI in the Insurance Industry
“According to data reported by MarketResearch.Biz, the global market size for generative AI in the insurance sector is on a remarkable growth trajectory. Projections indicate a substantial increase, with the market expected to surge from USD 346.3 million in 2022 to an impressive USD 5,543.1 million by 2032. This data underscores the immense potential and rapid expansion that generative AI is poised to achieve within the insurance industry, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.9% projected between 2023 and 2032.”
The growth in generative AI within the insurance sector can be attributed to the following key factors:
1. Automation and Enhanced Efficiency: Generative AI’s capability to automate various insurance tasks significantly improves operational efficiency. By streamlining operations and reducing human errors, it accelerates processes and enhances overall effectiveness.
2. Escalating Data Volume and Complexity: The insurance industry faces a continuous surge in data volume, leading to increased complexity. Generative AI plays a pivotal role in managing these vast and intricate datasets, extracting valuable insights. Its ability to effectively utilize extensive data sets serves as a major driving factor behind the growth of generative AI in the insurance market.
Highlighting the Differences Between Traditional and Generative AI in Insurance Operations: Key Differences
Generative AI and traditional AI represent distinct approaches within the realm of artificial intelligence, each offering unique capabilities and applications within the insurance sector. Grasping the disparities between generative AI and traditional AI is imperative for insurance professionals to fully harness the potential of these technologies and make well-informed choices regarding their adoption.
Traditional AI, often referred to as rule-based AI or narrow AI, operates on predefined rules and established patterns to execute specific tasks. It follows a deterministic approach, where the output is directly derived from the input and predefined algorithms. In contrast, generative AI relies on advanced algorithms and deep learning models, enabling it to generate fresh content and data. Unlike traditional AI, generative AI isn’t confined by rigid rules and has the capacity to produce original and dynamic outcomes.
Traditional AI is widely deployed in the insurance sector for specific tasks such as data analysis, risk assessment, and fraud detection. It delivers valuable insights and streamlines routine processes, enhancing operational efficiency. In contrast, generative AI introduces novel possibilities. It can synthesize data for training, augmenting limited datasets and bolstering the performance of AI models. Generative AI can also craft personalized insurance policies, simulate diverse risk scenarios, and facilitate predictive modeling.
Traditional AI models excel at scrutinizing structured data and identifying familiar patterns of fraudulent activities based on predetermined rules associated with risk assessment and fraud detection. In contrast, generative AI can enhance risk assessment by generating a spectrum of risk scenarios and detecting emerging patterns of fraud that may not be explicitly encoded in traditional rule-based systems. Additionally, generative AI empowers insurers to offer genuinely customized insurance policies, tailoring coverage, pricing, and terms based on individual customer profiles and preferences. While traditional AI can support personalized recommendations rooted in historical data, its capacity for crafting highly individualized content may be limited.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge that generative AI, owing to its complexity and ability to generate novel content, presents challenges related to ethical usage, fairness, and bias, necessitating careful attention to ensure responsible implementation. Traditional AI systems tend to be more transparent and easier to elucidate, which can be pivotal for regulatory compliance and ethical considerations.
Various Generative AI Models Applied to the Insurance Industry
Generative AI and traditional AI represent distinct approaches within the realm of artificial intelligence, each offering unique capabilities and applications within the insurance sector.
Grasping the disparities between generative AI and traditional AI is imperative for insurance professionals to fully harness the potential of these technologies and make well-informed choices regarding their adoption.
Traditional AI, often referred to as rule-based AI or narrow AI, operates on predefined rules and established patterns to execute specific tasks. It follows a deterministic approach, where the output is directly derived from the input and predefined algorithms. In contrast, generative AI relies on advanced algorithms and deep learning models, enabling it to generate fresh content and data. Unlike traditional AI, generative AI isn’t confined by rigid rules and has the capacity to produce original and dynamic outcomes.
Regarding data and training, traditional AI algorithms necessitate labeled data for training and heavily depend on human-crafted features. The performance of traditional AI models is contingent on the quality and quantity of labeled data available during training. Conversely, generative AI models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), can create new data without direct supervision. They glean insights from unlabeled data and can generate meaningful outputs that transcend the training data.
Generative AI models are designed to grasp and replicate patterns and structures inherent in their training data, enabling them to create novel samples resembling the original dataset. Within the domain of generative AI in insurance, three prominent generative model types stand out: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and autoregressive models.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs, introduced by Ian Goodfellow and colleagues in 2014, consist of two neural networks – the generator and the discriminator – engaged in a competitive game. The generator’s task is to produce synthetic data samples, while the discriminator aims to distinguish between real and synthetic samples. During training, the generator learns to generate data that becomes progressively harder for the discriminator to distinguish from real data. This iterative training process equips the generator to create highly realistic and coherent data samples.
In the context of insurance, GANs find utility in generating synthetic yet realistic insurance related data, such as policyholder demographics, claims records, or risk assessment data.
These generated samples augment existing datasets for training, improving the performance of various AI models used in insurance applications. For instance, insurers employ GANs to create synthetic insurance data, facilitating the training of AI models for fraud detection, customer segmentation, and personalized pricing. By generating lifelike synthetic data, GANs not only enhance data quality but also enable insurers to develop more accurate predictive models, thus enhancing the overall efficiency and precision of insurance operations.
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): VAEs, another generative model type, blend generative and inference elements. VAEs consist of two primary components: an encoder and a decoder. The encoder transforms input data into a latent space representation, while the decoder reconstructs data from the latent space into the original data space.
Unlike GANs, VAEs employ probabilistic methods for generating new samples. By sampling from the learned latent space, VAEs create data with inherent uncertainty, yielding more diverse samples compared to GANs. In insurance, VAEs prove valuable for generating diverse and innovative risk scenarios, aiding in risk assessment, portfolio optimization, and the development of novel insurance products.
Autoregressive Models: Autoregressive models are known for their sequential data generation approach, predicting one element at a time based on the probability distribution of each element given the preceding ones. In essence, these models forecast each data point based on previous data points. They are particularly suited for generating sequences or time-series data.
In the insurance sector, autoregressive models can generate sequential data, such as time-series data on insurance premiums, claims, or customer interactions. These models assist insurers in predicting future trends, detecting anomalies within data, and formulating data-driven business strategies. For example, autoregressive models can forecast future claim frequencies and severities, enabling insurers to allocate resources and proactively prepare for potential surges in claims. Additionally, these models support anomaly detection by identifying unusual patterns in claims data that may signal fraudulent activities. Leveraging autoregressive models empowers insurers to derive valuable insights from sequential data, optimize operations, and enhance risk management strategies.
In summary, the three primary generative model types – GANs, VAEs, and autoregressive models – offer distinct capabilities for generating new data in the insurance industry. GANs excel in producing highly realistic samples, VAEs provide diverse and probabilistic samples, while autoregressive models are well-suited for generating sequential data. Leveraging these potent generative models enables insurers to enhance data analysis, risk assessment, and product development, ultimately reshaping the insurance industry’s operational landscape.
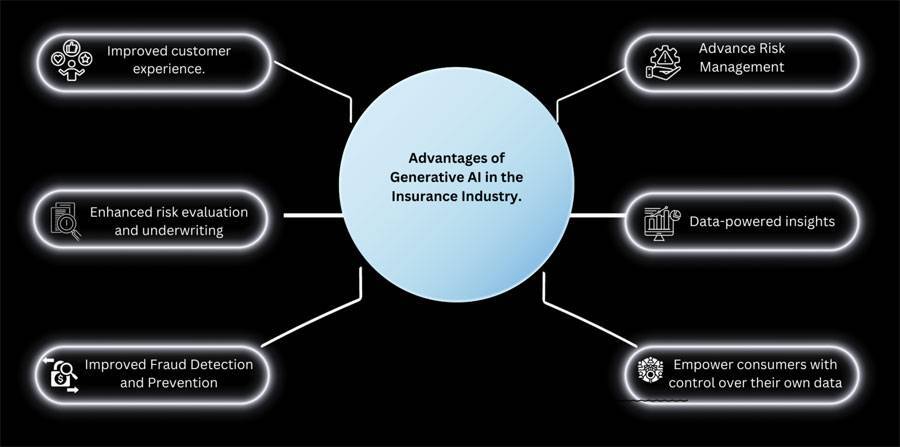
Advantages of Generative AI in the Insurance Industry
Generative AI is exerting a profound influence on the insurance sector, introducing a plethora of advantages that reshape insurers’ operations, customer engagement, and risk management. Below are key merits associated with the adoption of generative AI within the insurance industry:
Improved customer experience
Generative AI empowers insurers to provide customized experiences for their clientele. Through the analysis of vast amounts of customer data, AI algorithms can personalize insurance products to align with individual requirements and choices. Virtual assistants driven by generative AI engage in live interactions, assisting customers with policy inquiries and claims procedures, resulting in heightened satisfaction and bolstered customer allegiance.
Enhanced risk evaluation and underwriting
Generative AI models excel in performing more precise and efficient risk assessments and policy underwriting. By scrutinizing historical data and recognizing patterns, AI algorithms can forecast potential risks with heightened accuracy. This empowers insurers to fine-tune their underwriting choices, provide personalized coverage solutions, and mitigate the likelihood of adverse selection.
Improved Fraud Detection and Prevention
Sophisticated generative AI algorithms have the ability to spot patterns and irregularities linked to fraudulent activities, leading to early identification and prevention of deceptive insurance claims. Through the examination of extensive datasets, generative AI bolsters fraud detection prowess, safeguarding insurers from potential financial liabilities and upholding their reputation.
Advance Risk Management
Generative AI’s predictive modeling proficiency empowers insurers to simulate and predict diverse risk scenarios. By preemptively recognizing potential risks, insurers can formulate forward-looking risk management strategies, curtail losses, and optimize their risk portfolios with precision.
Data-powered insights
Utilizing generative AI-powered customer analytics yields invaluable intelligence on customer actions, market dynamics, and evolving vulnerabilities. This data-centric methodology enables insurance providers to craft pioneering solutions and offerings that align with evolving customer demands and inclinations, ultimately fostering a distinct competitive edge.
Enhanced cost-efficiency and operational optimization
Through the automation of diverse processes, generative AI diminishes the necessity for manual intervention, resulting in cost reductions and heightened operational effectiveness for insurance companies. Tasks such as automated claims handling, underwriting, and customer engagements liberate resources, enabling insurers to prioritize more strategic endeavors.
Ensuring regulatory compliance and fostering transparency
By integrating explainable AI (XAI) methods, generative AI ensures both transparency and adherence to regulatory requirements. This empowers insurance providers to comprehend the rationale behind AI-generated decisions, thereby facilitating compliance with regulatory mandates and bolstering customer confidence in AI-driven procedures.
Empower consumers with control over their own data
Generative AI streamlines the implementation of a zero-party data strategy for insurers, a proven approach that has been successful in various industries. This strategy harnesses information willingly shared by consumers in response to tailored, straightforward questions, enabling sales and marketing teams to gather data in a non-intrusive and transparent manner. As a result, insurers gain valuable insights from consumers, while consumers benefit from more personalized insurance solutions that enhance their protection.
Generative AI has the capacity to revolutionize the insurance sector by elevating customer experiences, enhancing risk evaluation and underwriting, simplifying claims handling, identifying and thwarting fraudulent activities, facilitating proactive risk management, offering data-driven insights, streamlining operations, stimulating innovation, and guaranteeing adherence to regulatory standards. These capabilities empower insurers to excel in a dynamic and evolving market landscape.
Applications of Generative AI in the Insurance Sector
Generative AI showcases a multitude of applications within the insurance sector, presenting innovative resolutions to enduring problems and instigating transformative shifts. Here are several prominent instances of generative AI utilization in the insurance industry:
Personalized insurance plans
Generative AI enables insurers to create personalized insurance policies tailored to individual customers’ needs and risk profiles. By analyzing vast datasets and customer information, AI algorithms generate customized coverage options, pricing, and terms, enhancing the overall customer experience and satisfaction. For instance, an auto insurer can utilize generative AI to analyze a customer’s driving history, vehicle details, and personal characteristics to offer a customized car insurance policy that aligns with the individual’s specific requirements.
Automated Underwriting
Generative AI revolutionizes the underwriting process through the automation of risk assessment and decision-making. By leveraging AI models, insurers can scrutinize past data, recognize patterns, and forecast potential risks, resulting in more precise and streamlined underwriting decisions. Take, for example, a life insurance provider that employs generative AI algorithms to scrutinize medical records, lifestyle information, and familial backgrounds. This approach expedites policy approvals, elevating customer satisfaction and overall efficiency.
Automated Claim Processing
Generative AI automates claims processing by extracting and validating data from claim documents, reducing manual efforts and processing time. Automated claims processing ensures faster and more accurate claim settlements, improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. For example, property insurers can utilize generative AI to automatically process claims for damages caused by natural disasters, automating the assessment and settlement for affected policyholders.
Detecting and preventing fraud
Generative AI plays a crucial role in the fight against insurance fraud by sifting through extensive data and spotting patterns that signal dishonest activity. With the assistance of AIdriven algorithms, insurers can swiftly pinpoint questionable claims as they occur, empowering them to proactively counter fraud and minimize financial harm. For instance, in the realm of health insurance, generative AI can detect irregularities within medical billing data, revealing possible fraudulent claims and leading to significant cost savings.
Helping customers with virtual assistants
Virtual assistants powered by Generative AI deliver immediate customer support, handling policy inquiries, providing updates on claim status, and addressing general insurance queries in real-time. These virtual assistants improve customer engagement while alleviating the workload of customer support teams. As an illustration, a property insurance firm could integrate a virtual assistant into its website, guiding customers through the claims procedure and furnishing valuable information.
Risk Assessment and Predictive Analysis
Generative AI models simulate diverse risk scenarios and forecast future risks, assisting insurers in refining their risk management strategies and informed decision-making. Predictive analytics, powered by generative AI, offers valuable insights into emerging risks and market trends. As an example, a property and casualty insurer can leverage generative AI to predict weather-related risks across various regions, enabling preemptive measures to mitigate potential losses.
Fostering Innovation in Product Development
Generative AI fosters innovation and advances product development by generating novel concepts and pinpointing unmet needs within the insurance sector. AI-driven insights empower insurers to craft fresh insurance offerings that align with evolving customer demands and preferences. For instance, a travel insurance firm can harness generative AI to scrutinize travel patterns and customer inclinations, resulting in the formulation of custom-tailored insurance packages for distinct travel destinations.
Applications of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Generative AI utilizes NLP for handling unstructured data, including customer feedback, social media interactions, and medical records, to extract valuable insights. With the assistance of NLPdriven sentiment analysis, insurers can grasp customer sentiments and enhance their services accordingly. For example, an insurance company can apply NLP-powered sentiment analysis to comprehend customer attitudes regarding their offerings, thereby facilitating improvements based on customer input.
Detecting anomalies
Generative AI’s ability to detect anomalies enables insurers to spot unusual data patterns, like atypical customer behavior or questionable claims. Identifying anomalies early on aids in risk mitigation and enhances decision-making precision. Consider an auto insurance company employing generative AI to uncover unusual claims patterns, such as a sudden spike in accident claims within a particular region. This enables the detection of potential fraud or emerging risks.
Analysis of images and videos
Generative AI is proficient at scrutinizing images and videos to evaluate damages in insurance claims, whether stemming from vehicle accidents or property incidents. This visual analysis expedites the claims processing timeline and ensures precise loss assessments. For instance, a car insurance provider can employ image analysis to gauge repair expenses following a car accident, streamlining the claims settlement process for policyholders while maintaining accuracy.
Real-world examples of insurance companies applying generative AI
Generative AI is quickly transforming the insurance sector, providing significant opportunities for operational enhancements, data-driven decision-making, and improved customer interactions. Within this industry, five insurance enterprises distinguish themselves for their proactive adoption of generative AI:
GEICO (USA) : GEICO, a leading auto insurance provider, has created an intuitive virtual assistant to aid potential and existing customers in addressing insurance-related inquiries. This virtual assistant engages in dialogues and furnishes vital details, utilizing message intent recognition to comprehend specific questions and furnish pertinent links. While the virtual assistant doesn’t directly create insurance quotes, it guides users to relevant sales pages for actions such as requesting a quote. GEICO’s inventive integration of generative AI in their virtual assistant elevates customer interaction and enhances the overall user journey.
Chubb : Chubb, with its headquarters situated in Zurich, Switzerland, stands as a renowned global insurance firm that provides a wide spectrum of insurance solutions. With a keen eye on the possibilities offered by generative AI, Chubb is poised to deploy these state-of-the-art tools extensively. Their strategic emphasis centers on harnessing AI-driven innovations to augment vital functions like underwriting and claim processing. Through the adoption of generative AI technology, Chubb aims to streamline operations and reinforce its commitment to innovation within the insurance sector.
Liberty Mutual : Headquartered in Chicago, USA, Clearcover is a prominent digital car insurance provider specializing in Auto Insurance. With a notable investment of around $329.5 million, the company leads the way in insurance innovation. Clearcover utilizes advanced technology to present a distinctive offering of competitive prices and a seamless customer journey. At the heart of their strategy lies ClearAI, an AI-driven tool automating the claims procedure. Through ClearAI, clients experience prompt and efficient assistance, streamlining the claims resolution and ultimately elevating overall customer contentment. As a trailblazer in the realm of digital insurance, Clearcover consistently showcases its dedication to leveraging technology for redefining the car insurance landscape.
Ping An Insurance : Shenzhen, China, serves as the headquarters for Ping An Insurance, a distinguished global entity offering an extensive array of services encompassing life insurance, property and casualty insurance, banking, and financial services. The company displays a steadfast commitment to pioneering technologies, notably AI, big data, and cloud technologies. Particularly noteworthy are Ping An’s AI-powered ventures, which incorporate generative models pivotal to critical facets of their operations, including underwriting, risk assessment, and automated customer service. Through the integration of these cutting-edge AI technologies, Ping An Insurance solidifies its position at the vanguard of innovation within the insurance and financial services sectors, striving to deliver efficient and customized solutions to their diverse clientele.
SWICA (Switzerland) : SWICA, a health insurance provider, has designed an advanced chatbot for customer support. This chatbot not only addresses common queries but also smoothly manages policy modifications directly within the chat interface. Customers can undertake multiple tasks, like adjusting deductibles, updating addresses, requesting insurance cards, adding accident coverage, and enrolling new family members, all without navigating to a separate page. SWICA’s chatbot showcases the effective application of generative AI in enriching customer satisfaction and simplifying policy administration procedures.
Insurify (USA) : Insurify, a platform for comparing insurance options, was among the pioneers in incorporating chatbots within the insurance sector. Their chatbot employs natural language processing and machine learning technologies to engage users with precise queries, aiding them in identifying the most suitable insurance policy according to their requirements. Impressively, the bot can analyze images, including snapshots of license plates, in addition to text inputs. Functioning seamlessly within the Facebook Messenger app, Insurify’s chatbot showcases a successful fusion of generative AI, facilitating effortless interactions and tailored policy suggestions.
Lemonade (USA) : Lemonade, a pioneering insurance company powered by AI, offers an intuitive chatbot that seamlessly navigates policyholders throughout their entire customer journey. Users can easily apply for policies, complete payments, file claims, and receive instant updates without resorting to phone communication. A standout achievement for Lemonade is the world record set by their chatbot, Maya, for processing and approving a $979 claim in under 3 seconds. This extraordinary accomplishment underscores Lemonade’s innovative application of generative AI in delivering prompt, real-time customer assistance and expedited claims processing.
Through the integration of generative AI, these enterprises anticipate a multitude of advantages, including tailored offerings, swift claim resolutions, and impartial risk evaluations, ultimately driving higher levels of customer contentment.
Prospects of generative AI in the insurance industry
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the insurance sector, generative AI has demonstrated its capability to seamlessly assimilate into various processes, offering the potential to redefine them. Its impact on the industry, spanning risk assessment, fraud detection, customer service, and product development, has been noteworthy. Looking ahead, the trajectory of generative AI in insurance holds the promise of being highly dynamic and disruptive, paving the way for novel advancements and extensive opportunities.
Automated Claim Processing: Looking ahead, generative AI in the insurance domain will witness a substantial transition towards autonomous claims processing. By seamlessly blending advanced computer vision and natural language processing capabilities, AI-driven systems will adeptly handle and authenticate claims without the need for human involvement. This evolution will bring about accelerated and precise settlements for customers, effectively diminishing the time and effort required for claiming and processing.
Advanced fraud detection and prevention: The future of generative AI in insurance is poised to bolster fraud detection and prevention capabilities. AI algorithms, combined with anomaly detection techniques, will accurately pinpoint fraudulent patterns and activities, leading to a substantial decrease in losses attributed to insurance fraud. Constant monitoring in real-time and intelligent algorithms will serve as a formidable defense against continually evolving fraudulent schemes.
Integrating IoT with Generative AI: The convergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) and generative AI is poised to establish a cohesive ecosystem comprising interconnected devices and data. Within this framework, insurers can harness data gleaned from smart devices like connected vehicles, wearables, and home sensors. This enables them to perform precise risk assessments, customize policies in real-time, and proactively mitigate losses by providing personalized safety guidance.
Leveraging Explainable AI (XAI) to enhance transparency: With the increasing adoption of generative AI in the insurance industry, there will be a heightened need for Explainable AI (XAI). XAI methods will play a pivotal role in upholding transparency, adhering to regulatory requirements, and fostering trust in decisions made by AI systems. Insurers will be required to elucidate the inner workings of AI algorithms, offering insights into how specific recommendations or decisions are reached. This commitment to transparency not only enhances customer comprehension but also ensures compliance with regulatory standards. Automated Customer Engagement: Generative AI is poised to revolutionize how customers interact with insurers, introducing advanced chatbots and virtual assistants. These AI-driven assistants will adeptly manage routine inquiries and engage in sophisticated dialogues, comprehending intricate customer requirements and delivering tailored policy recommendations and coverage options.
Advancements in Risk Modeling and Underwriting: In the forthcoming era of generative AI within the insurance sector, we can anticipate remarkable progress in the domains of risk modeling and underwriting. Insurers will leverage the capabilities of generative models to simulate and predict diverse risk scenarios, thereby enhancing the precision of underwriting decisions and optimizing their portfolios to attain greater profitability.
Strategic Alliances and Collaborations: To unlock the complete potential of generative AI, insurers will strategically form alliances and engage in collaborations with technology companies, data providers, and insurtech startups. These strategic partnerships will serve as conduits to cutting-edge technologies, extensive data sources, and domain expertise. As a result, insurers can expedite innovation and maintain a competitive edge in the market by leveraging these collaborative efforts.
Ethical AI Practices and Regulatory Compliance: As generative AI becomes more pervasive in the insurance industry, ensuring ethical AI practices and adherence to regulatory guidelines will be paramount. Insurers will be required to adopt robust governance frameworks to address bias, fairness, and privacy concerns associated with AI algorithms.
Health and well-being are coming together: The merging of health and well-being trends goes hand in hand with the use of generative AI to enhance comprehensive and personalized healthcare. Insurers can use AI-generated insights to create tailored health insurance plans that encourage healthier living, ultimately lowering claims expenses and enhancing customer loyalty. Generative AI’s capacity to analyze health data and predict risks empowers insurers to craft wellness programs customized to the unique requirements of their policyholders.
Accessible insurance: The integration of generative AI into the insurance sector aligns seamlessly with the drive for inclusive insurance. With AI’s data processing capabilities, insurers can pinpoint overlooked markets and demographics, such as low-income households, migrants, and small businesses. By reaching out to these underserved groups, insurers help close the insurance gap, fostering financial security and stability for a wider population.
Generative AI’s future in insurance holds great potential, revolutionizing how the industry functions, engages with clients, and handles risks. By embracing generative AI in a balanced manner, insurers can tap into unparalleled levels of efficiency, customer contentment, and profitability within the ever-evolving insurance landscape.
Conclusion
Generative AI has had a significant impact on the insurance industry, bringing numerous benefits to both insurers and customers. It has automated business processes, improved operational efficiency, provided personalized customer experiences, and enhanced risk assessment. Leading insurers like Lemonade, SWICA, and GEICO have shown how generative AI can streamline customer interactions, facilitate policy management, and expedite claim processing. As this technology continues to advance, insurers stand to achieve new levels of innovation by offering customized insurance solutions, proactive risk management, and improved fraud detection.
Nevertheless, adopting generative AI also necessitates a focus on data privacy, regulatory compliance, and ethical considerations. With a balanced approach, the future of generative AI in insurance holds great promise, ushering in an era of increased efficiency, customer satisfaction, and profitability in the ever-evolving insurance landscape.